Injection Molding: Processes, Benefits, Applications, and Future Trends
2024-02-26 16:18:52
Plastic injection molding is a basic technology of modern manufacturing, characterized by accuracy and efficiency in producing a wide range of products. Despite its widespread use, the complexities of this practice are difficult to understand. This in-depth guide offers a comprehensive exploration of injection molding, covering its process, applications, defects, materials, and solutions, tailored specifically for engineers, plant managers, and manufacturers looking to optimize performance and yield in real-world operations.
Injection molding is a high-volume manufacturing process used to produce precision plastic parts by injecting molten thermoplastic or thermoset injection molding material into a mold cavity. It is widely recognized for its ability to deliver consistent quality, tight tolerances, and fast cycle times, making it indispensable in sectors such as automotive, electronics, packaging, and medical devices.
Further reading: What are Fundamentals of Injection Molding? 3 Keys to Injection Molding Plant
Advantages of Injection Molding
Injection molding is preferred for manufacturers looking to achieve scale, accuracy, and repeatability. Core benefits include:
- High Productivity and Throughput: Cycle times can be as low as 10 seconds, depending on small and thin products, allowing for rapid production of thousands of identical parts.
- Low Unit Cost at Scale: As volume increases, per-part cost drops significantly, especially when reusing aluminum or hardened steel molds.
- Excellent Repeatability: Precision molds and controlled process parameters ensure part-to-part consistency, which is vital for quality-sensitive industries.
- Material Flexibility: Supports a broad range of materials, including PP, ABS, PC, LSR, and bio-polymers, with optional fillers and colorants.
- Minimal Post-Processing: Most molded parts emerge with smooth, finished surfaces that require little to no secondary operations.
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Scrap material is often recyclable, supporting green manufacturing initiatives.
- Complex Part Geometry: Molded parts can feature intricate internal and external details, undercuts, and threads.
Disadvantages of Injection Molding
Despite its benefits, injection molding comes with limitations:
- High Tooling Costs: Mold design and fabrication can be expensive, especially for multi-cavity or complex geometries.
- Extended Lead Times: Creating a custom mold may take several weeks, delaying project kickoff.
- Design Limitations: Wall thickness, gate placement, and draft angles must be optimized for moldability.
- Unsuitable for Low Volumes: For small batch runs, methods like 3D printing or CNC machining may be more economical.
The injection molding process consists of six key stages that ensure repeatable, high-quality part production:
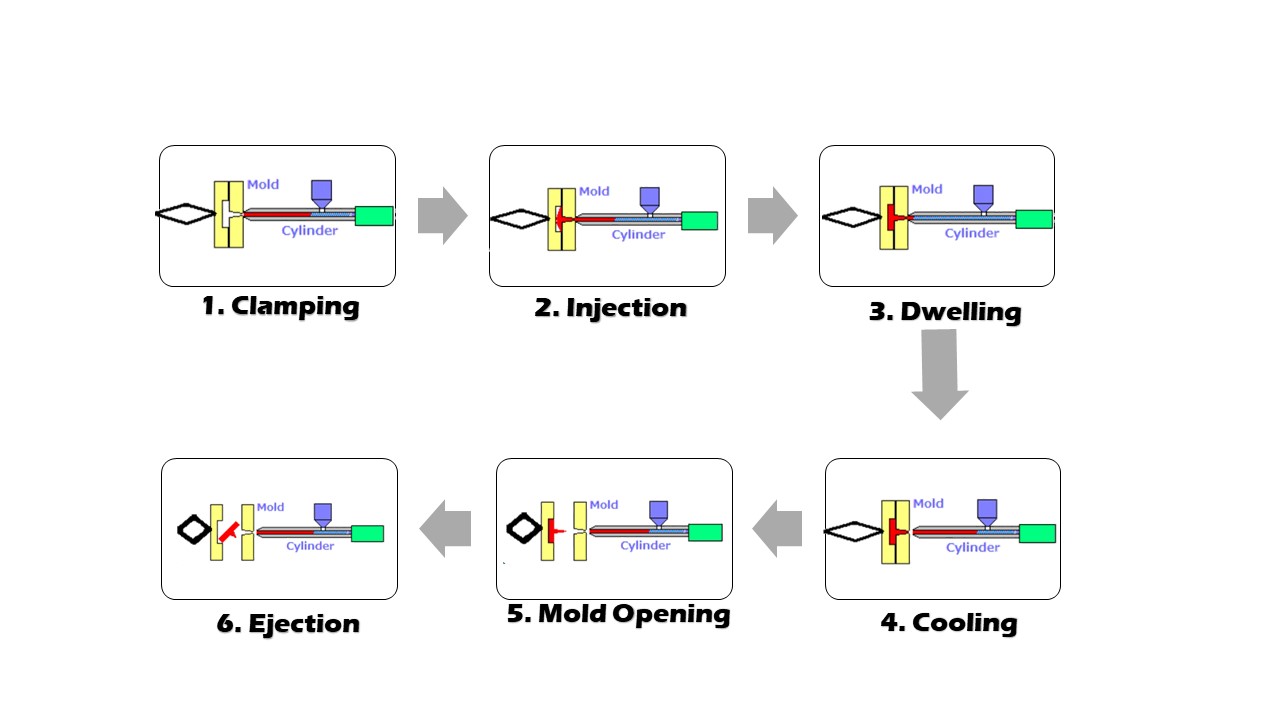
Step 1: Clamping
The two halves of the mold are securely closed using a clamping unit. Hydraulic or electric systems apply the necessary force to shut the mold under injection pressure tightly.
Step 2: Injection
Pre-heated plastic pellets are melted in the barrel and injected into the mold cavity at high pressure via the screw and nozzle system.
Step 3: Dwelling (Holding)
Holding pressure is applied once the cavity is filled to compensate for shrinkage and ensure the part fully conforms to the mold geometry.
Step 4: Cooling
Cooling systems embedded in the mold extract heat, allowing the plastic to solidify. Proper cooling ensures dimensional accuracy and mechanical strength.
Step 5: Mold Opening
The clamping unit releases the mold halves, preparing the part for removal.
Step 6: Ejection
Ejector pins push the cooled part out of the mold. Any burrs or excess material are trimmed to meet final specifications.
Quality output in injection molding is determined by a balance of materials, mold design, machinery, and precise control.
Material and Mold Design Selection
The success of your injection molding program depends on several key factors, including:
Material Selection
Each application demands careful evaluation of material properties:
- ABS: Excellent for electronics, toys, and enclosures.
- PA (Nylon): Ideal for gears, bearings, and automotive parts due to its toughness and thermal resistance.
- PET/RPET: Commonly used in food-safe applications and sustainable packaging.
Further reading: Comprehensive Guide to Top 10 Injection Molding Materials and Their Properties
Mold Design
Efficient mold design improves output and reduces cycle time:
- Gating System: Controls melt flow and pressure distribution.
- Cooling Channels: Ensure uniform heat extraction.
- Venting: Prevents trapped air and burn marks.
- Draft Angles: Simplify part ejection and reduce wear.
Choosing the Right Injection Molding Machine
Selecting a injection molding machine with suitable specifications is critical:
Machine Parameters
- Clamping Force: Must match mold size and projected area.
- Shot Size: Should accommodate material volume without degradation.
- Cycle Time: Impacts production efficiency and cost.
Process Control
Advanced machines offer real-time monitoring and auto-adjustment features for pressure, temperature, and screw position. These capabilities reduce waste and improve first-pass yield.
Injection molding delivers tailored solutions for diverse market sectors:
Construction
- Durable, lightweight components for plumbing, electrical, and structural fixtures.
- Cost-effective alternatives to wood and metal.
- Common parts: anchors, conduit fittings, and tool handles.
Food & Beverage
- Compliant with FDA and GMA-Safe standards.
- BPA-free, non-toxic plastics for containers and process parts.
- Common parts: bottle caps, conveyor guides, mixing paddles.
Further reading: Replacing Melamine and Acrylic: The Rise of PET/RPET Tableware in Affordable Markets
Further reading: The Science Behind Plastic Caps: How are Plastic Bottle Caps Made
Medical
- Uses medical-grade, biocompatible resins.
- Ideal for single-use and reusable components.
- Common parts: syringes, diagnostic kits, surgical tools.
Automotive
- Parts must meet high standards of durability and safety.
- Molded components reduce weight while maintaining integrity.
- Common parts: air ducts, dashboards, trim panels.
Further reading: Injection Molding Machine: Key to Precision Manufacturing of Automotive Parts
Retail and Displays
- Customizable for branding and aesthetics.
- Sturdy, clean parts ideal for high-touch environments.
- Common parts: shelf hooks, POP displays, signage clips.
Modern molding techniques extend capabilities beyond traditional processes:
- 2k Injection Molding: This technique allows parts to be produced using multiple materials in a single mold, resulting in improved functionality and aesthetics.
- Insert Molding: During the process, existing components, such as B. Metal inserts, are embedded into the molded part to increase strength or add specific functionality.
- Overmolding: Overmolding forms a layer of plastic around an existing part to create a protective or decorative exterior.
- In Mold Labeling (IML): This technique integrates decorative elements directly into the molded part, eliminating the need for a secondary finishing process.
- Two-Platen Molding: This configuration uses a two platen injection machine to clamp the mold. This allows for larger geometries and produces larger parts than 3-plate molding.
Other Articles Related to Injection Molding
We keep writing articles to share knowledge about injection molding technology.
- Vertical Injection Molding vs Horizontal Injection Molding for Plastic Components
- PET Preform Molding Solution: A Detailed Guide to PET Preform Manufacturing
- Microcellular Foam Injection Molding: Achieving Maximum Weight Reduction and Dimensional Stability
- Automotive Injection Molding: Process, Benefits, and Key Applications
- Thermoplastic Injection Molding Explained: How It Works & Why It’s Essential
- Thermoset Injection Molding: Process, Benefits & Applications
- Tooling Complexity: Complicated mold geometries require expert engineering.
- Maintenance Needs: Molds must be cleaned and serviced regularly.
- Shrinkage Control: Material behavior during cooling must be predicted and managed.
Sustainable Materials
Biodegradable polymers and recyclable resins are becoming mainstream as regulations tighten and consumer awareness grows.
Smart Automation
Real-time data from HMI and IoT systems enable predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization.
Related product: Smart Factory Management -HFM
Related product: Automation System
Globalization & Customization
Indian manufacturers are now expected to deliver globally competitive quality with locally adapted solutions for mass customization.
Further reading: Sustainable Injection Molding Manufacturing: Two-Platen Injection Machine for Global Markets
Injection molding is the cornerstone of precision plastic manufacturing. With its unmatched scalability, material versatility, and evolving technologies, it remains the preferred choice for delivering high-performance parts in demanding industries.
Your Trusted Injection Molding Partner
As the future of manufacturing shifts toward smart factories and sustainable solutions, choosing the right partner is more important than ever. Huarong, as an injection machine manufacturer, offers advanced injection molding machines, tailor-made automation solutions, and decades of experience to help you achieve production success.
Contact Huarong to learn how we can support your plastic part manufacturing journey—from concept to commercialization.
- Group Name: Huarong Group
- Brand: Huarong, Yuhdak, Nanrong
- Service Offerings: Injection Molding Machine, Vertical Injection Molding Machine, Injection Molding Automation
- Tel: +886-6-7956777
- Address: No.21-6, Zhongzhou, Chin An Vil., Xigang Dist., Tainan City 72351, Taiwan
- Official Website: https://www.huarong.com.tw/