What Is Insert Molding? Process, Advantages and Applications
2024-03-19 14:34:50
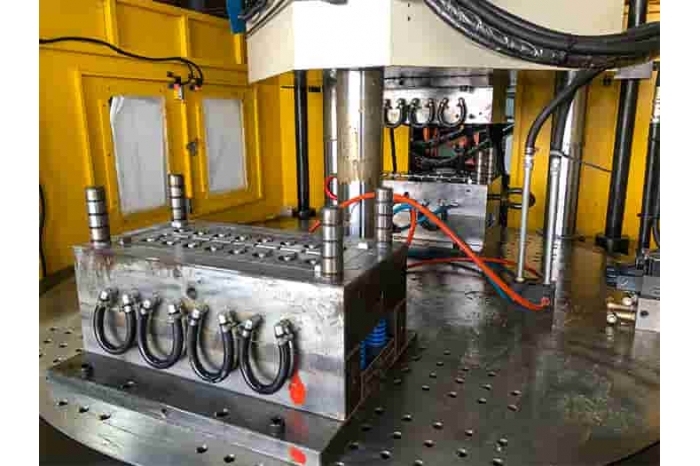

Insert molding is a specialized injection molding technique that involves encapsulating a pre-placed insert, typically a metal or different plastic component, with molten resin to form a single integrated part. This method is widely used in various industries particularly for products requiring a combination of metal and plastic parts. In this article, we will explore the insert molding process, its advantages, applications, and important factors to consider before implementing it.
Insert molding involves placing a pre-placed insert, such as metal components, into a mold cavity before injecting plastic. The molten plastic bonds to the insert in this process, creating a single, integrated part with enhanced durability and functionality. Common applications include creating metal attachment features for fasteners and reducing the need for additional assembly steps.
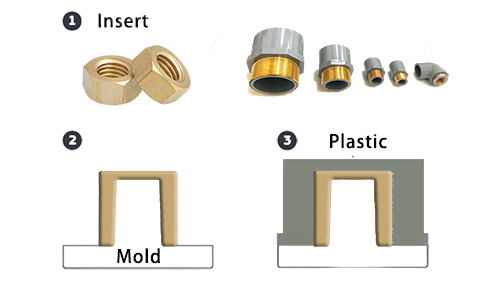
Insert molding is a multifaceted procedure that demands precision and meticulous planning. The process can be divided into several key stages, each critical to ensuring the quality and consistency of the final product.
1. Design and Material Selection
The initial phase involves designing the insert and selecting appropriate materials. The insert material should be compatible with the overmolding resin to ensure a robust bond. Common materials include metals like brass and aluminum, and engineering plastics.
2. Insert Placement
Accurate placement of the insert into the mold is crucial. This can be done manually or through automated systems. The position of the insert affects the structural integrity and functionality of the finished product. Automation in insert placement enhances precision and reduces human error.
- Manually Insert: Operators manually place inserts into the mold before the injection molding process. It is suitable for low—to medium-volume production runs.
- Automated Insert: This method involves using robotic arms or automated machinery to place inserts into the mold cavity, ensuring consistency, efficiency, and precision, though initial costs may be higher.

3. Mold Design
The mold must be designed to accommodate the insert and ensure proper flow of the molten resin around it. Cooling channels and ejection mechanisms must be carefully planned to avoid defects and facilitate smooth production.
4. Injection Molding
Once the inserts are in place, the molten resin is injected into the mold cavity, encapsulating the insert. The process parameters, such as injection speed, pressure, and temperature, are meticulously controlled to achieve optimal results. The resin solidifies around the insert, forming a cohesive unit.
Further reading: What is Injection Molding? Its Process, Advantages, Applications
5. Cooling and Ejection
Once the resin has sufficiently cooled and solidified, the molded part is ejected from the mold. Cooling time must be carefully managed to prevent warping or other defects. Automated systems can further streamline this process, ensuring consistency and efficiency.

6. Separating Sprue
If the mold is a cold-runner design, the framework that supports the part during molding will be leftover and attached to the part. This excess material, called sprue, is typically recycled for future use. Operators separate the sprue from the molded part to complete the manufacturing process.
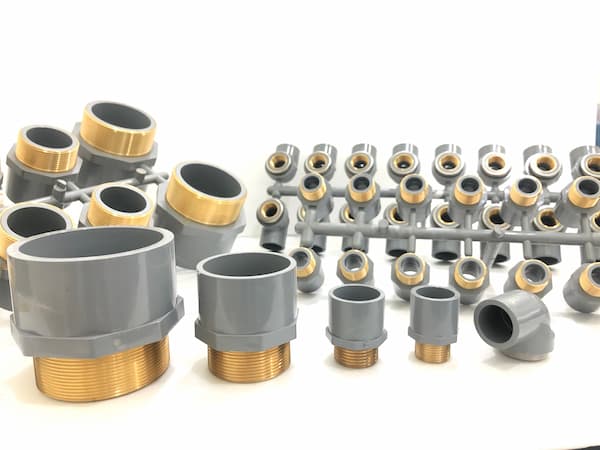

Insert molding offers numerous benefits, making it a preferred method for creating complex parts with enhanced functionality.
- Enhanced Structural Integrity: Insert molding produces parts with superior strength and durability by combining different materials. The strong bond between the insert and the resin provides better mechanical properties than parts made from a single material.
- Reduced Assembly Time: Insert molding eliminates the need for secondary assembly operations. The insert is molded directly into the part, reducing labor costs and increasing production efficiency.
- Design Flexibility: This process allows for greater design flexibility. Engineers can incorporate multiple functions into a single part, such as electrical connectivity, mechanical strength, and aesthetic appeal.
- Cost Efficiency: Despite the initial setup costs, insert molding can be cost-effective in the long run. The reduction in assembly time, combined with the high quality and durability of the parts, leads to significant cost savings.
Insert molding is widely used across various industries due to its versatility and effectiveness.
- Automotive Industry: In the automotive sector, insert molding is used to produce components that require a combination of plastic and metal, such as gears, shafts, and electrical connectors. These parts benefit from the strength and durability provided by the insert, ensuring reliable performance in demanding conditions.
- Consumer Electronics: Insert molding is integral to the manufacturing of consumer electronics, where precision and functionality are paramount. It is used to create housings, connectors, and other components that require intricate designs and robust performance.
Successful case of dental flosser: How to Manufacture High-Quality Dental Flossers and Interdental Brushes
- Medical Devices: The medical industry relies on insert molding to produce parts that meet stringent regulatory standards. This includes components for diagnostic equipment, surgical instruments, and other medical devices that require high precision and reliability.
Video of drive medical CPAP tubing production: Vertical Medical Injection Molding Machine -Drive Medical CPAP Tubing
- Aerospace and Defense: In aerospace and defense, insert molding is used to manufacture lightweight yet strong components that can withstand extreme conditions. This includes connectors, fasteners, and other critical parts that ensure the safety and efficiency of aerospace systems.
The field of insert molding continues to evolve, with new technologies enhancing precision, efficiency, and capabilities.
- Automated Systems: Automation has revolutionized insert molding, particularly in the placement of inserts and the handling of molded parts. Robotic systems ensure precise placement and consistent production, reducing the likelihood of defects and improving overall efficiency. Huarong Group has an automation department to customize customer's automation needs.
- Advanced Materials: The development of advanced materials, including high-performance plastics and composites, has expanded the possibilities of insert molding. These materials offer improved mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, enabling the production of parts for increasingly demanding applications.
- Simulation and Modeling: Modern software tools allow engineers to simulate and model the insert molding process, optimizing design and process parameters before actual production. This reduces the trial-and-error phase, saving time and resources.
While both processes of insert molding and overmolding involve molding plastic around other components, their primary differences lie in application and execution. Insert molding integrates metal components for structural enhancement, while overmolding focuses on adding layers of different plastics for improved functionality and aesthetics.
Further reading: What Is Overmolding? Its Process and Example vs Insert Molding
What are common materials for inserts?
- Thermoplastic Resins: The injection molding materials below offer varying degrees of strength, sturdiness, and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for various applications.
- Thermoplastics: Polypropylene (PP), Nylons (Polyamides/PA), Polycarbonate (PC), ABS, Polyethylene (PE), and Acetal.
- Thermosets: Polyester, Epoxy, Melamine-formaldehyde resins, and Urea-formaldehyde resins.
- Elastomers: Polyurethane, Natural rubber.
- Metal Inserts: Metal inserts such as stainless steel or brass can be used for applications requiring additional strength or conductivity. These inserts provide the necessary properties for products that withstand high temperatures or heavy loads.
Is insert injection molding suitable for large parts?
Insert injection molding can be used for large parts, but due to the complexity of the process, it is more commonly used for smaller, more intricate components.
Further reading: Large Part Injection Molding|Plastic Machine Experts
What factors need to be considered before inserting molding?
- Placement of Inserts: Placement within the mold is crucial for ensuring proper adhesion and functionality of the final part. The placement affects the forces acting on the insert and influences the amount of plastic needed to hold it securely.
- Minimizing the Gap Between Metal Part Insert: To prevent defects such as flash and voids, minimizing the gap between the metal part and the plastic during molding is essential. Besides, a narrower gap improves the reliability of the composite product molding, ensuring a more robust final product.
- Selecting the Right Resin and Molding Conditions: Choosing the right resin and molding conditions is vital, especially for delicate products like electrical parts, glass, and coils. Proper resin selection ensures the insert's sealing and fixation within the molded part.
- Choosing the Proper Mold: The design and construction of the mold play a significant role in the success of the insert molding process. The mold not only shapes the molten material but also secures the insert during molding. The mold must be designed to hold the inserts securely throughout the process.
- Cost Considerations: While insert molding offers many benefits, the cost implications, including the cost of the inserts themselves and the expenses associated with contracting an operator, must be considered. Additionally, understanding the potential increase in the piece price due to adding inserts is crucial for cost-sensitive parts.
- Production Volume Planning: The production volume requirements will determine the most suitable insert molding process between manual and automated loading. Conducting a cost-benefit analysis and understanding the production needs will help select the right loading method with the suitable injection molding machine.
What is an insert molding machine?
An insert molding machine is a specialized equipment designed to hold metal inserts in place while injecting plastic around them. This machine ensures precise placement and bonding of materials, efficiently producing durable and integrated components. Vertical injection molding machines are ideal machines for insert molding. Insert molding involves placing a pre-formed insert into the mold before injecting plastic around it. Vertical machines simplify this process as the mold opens vertically, making it easier for operators or automated systems to accurately place the inserts. In addition, vertical machines often have better cycle times for insert molding applications due to their table design, which allows for efficient handling and reduces the need for manual adjustments. This efficiency leads to higher productivity and lower labor costs.
Further reading: Comprehensive Guide to Vertical Injection Molding Machines
Insert molding is a powerful technique that combines precision, efficiency, and versatility. By understanding and optimizing each stage of the process, from design to production, manufacturers can produce high-quality parts that meet the demanding requirements of various industries. As technology advances, the possibilities for insert molding are expanding, offering even greater potential for innovation and excellence in manufacturing. If you are searching for an experienced injection molding machine manufacturer for insert molding requirements, please contact Huarong.
- Group Name: Huarong Group
- Brand: Huarong, Yuhdak, Nanrong
- Service Offerings: Injection Molding Machine, Vertical Injection Molding Machine, Injection Molding Automation
- Tel: +886-6-7956777
- Address: No.21-6, Zhongzhou, Chin An Vil., Xigang Dist., Tainan City 72351, Taiwan
- Official Website: https://www.huarong.com.tw/
Previous news : Vertical Injection Molding vs Horizontal Injection Molding for Plastic Components
Next news : Two Platen and Three Platen Injection Molding Machine Difference

