Robotic Arms in Manufacturing: Boosting Efficiency and Precision
2025-10-15 10:20:28

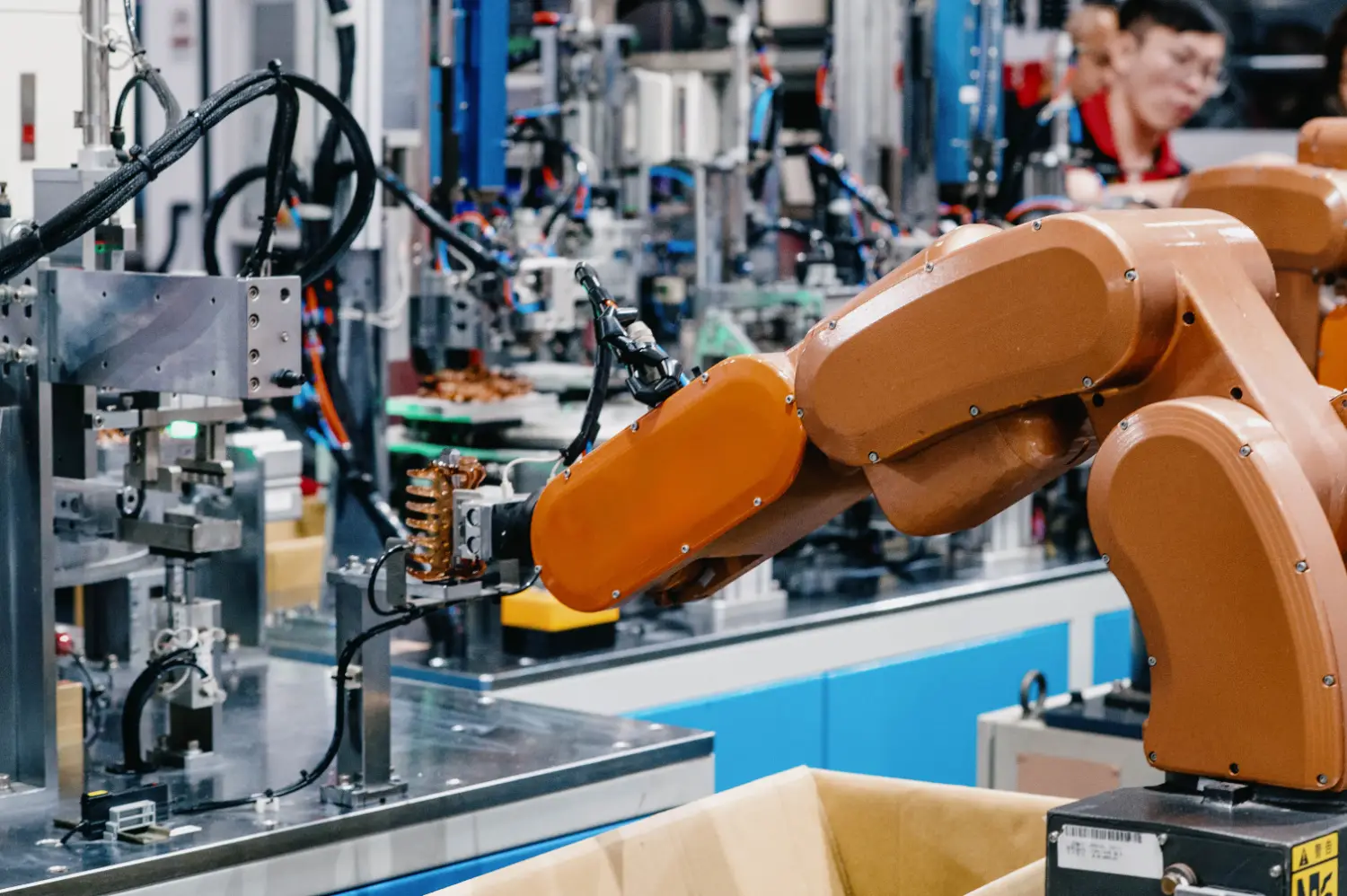
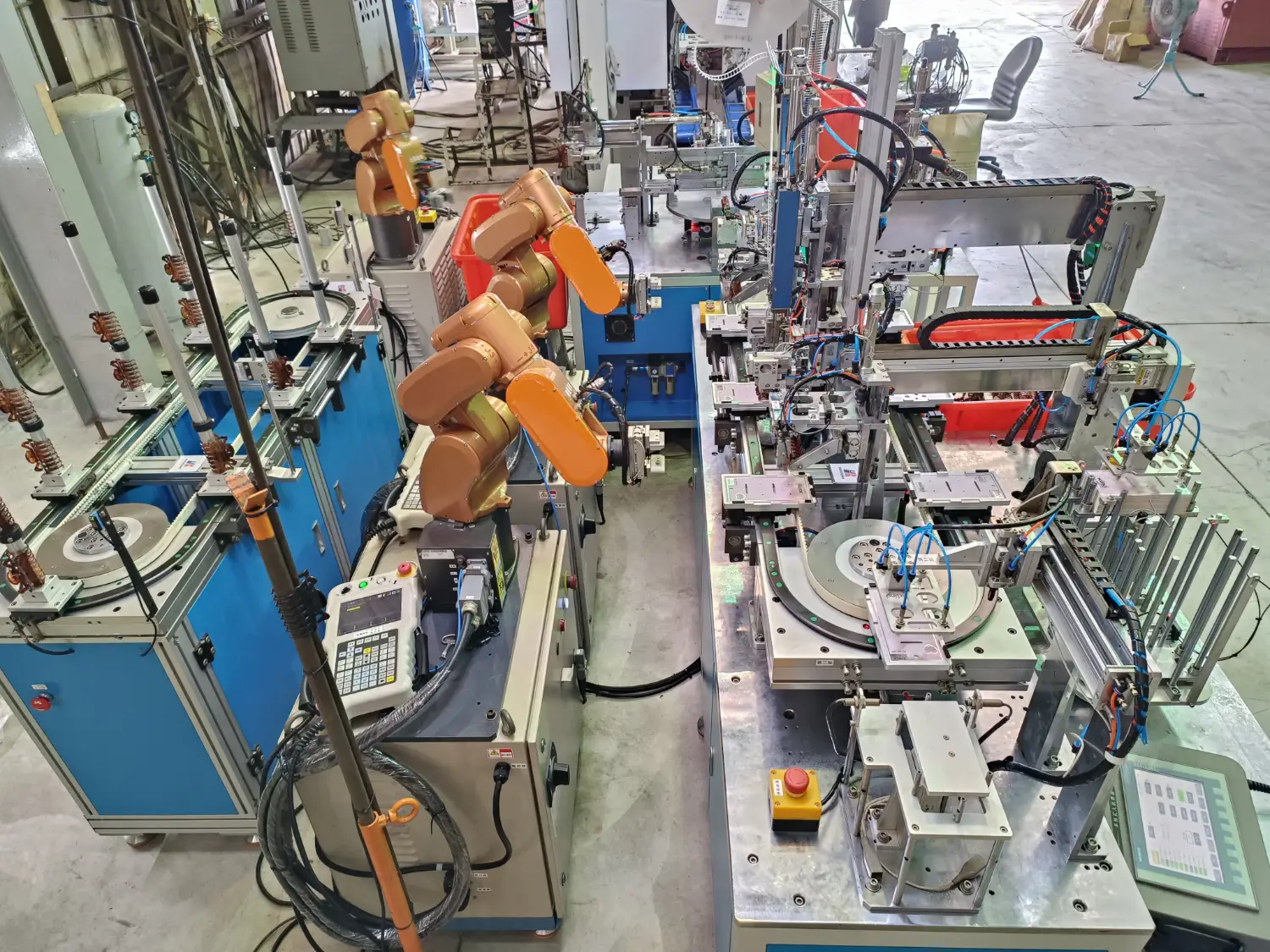
Robotic arms have become essential in modern manufacturing, performing tasks such as handling, assembly, welding, spraying, and inspection with high precision and consistency. Integrated with AI, sensors, and automation control systems, they deliver faster cycles, lower defects, and safer production environments. Today, industries such as automotive, electronics, medical, food, and aerospace rely on robotic arms to achieve stable quality, reduced labor, and smarter operation—making them a core driver of high-efficiency manufacturing.
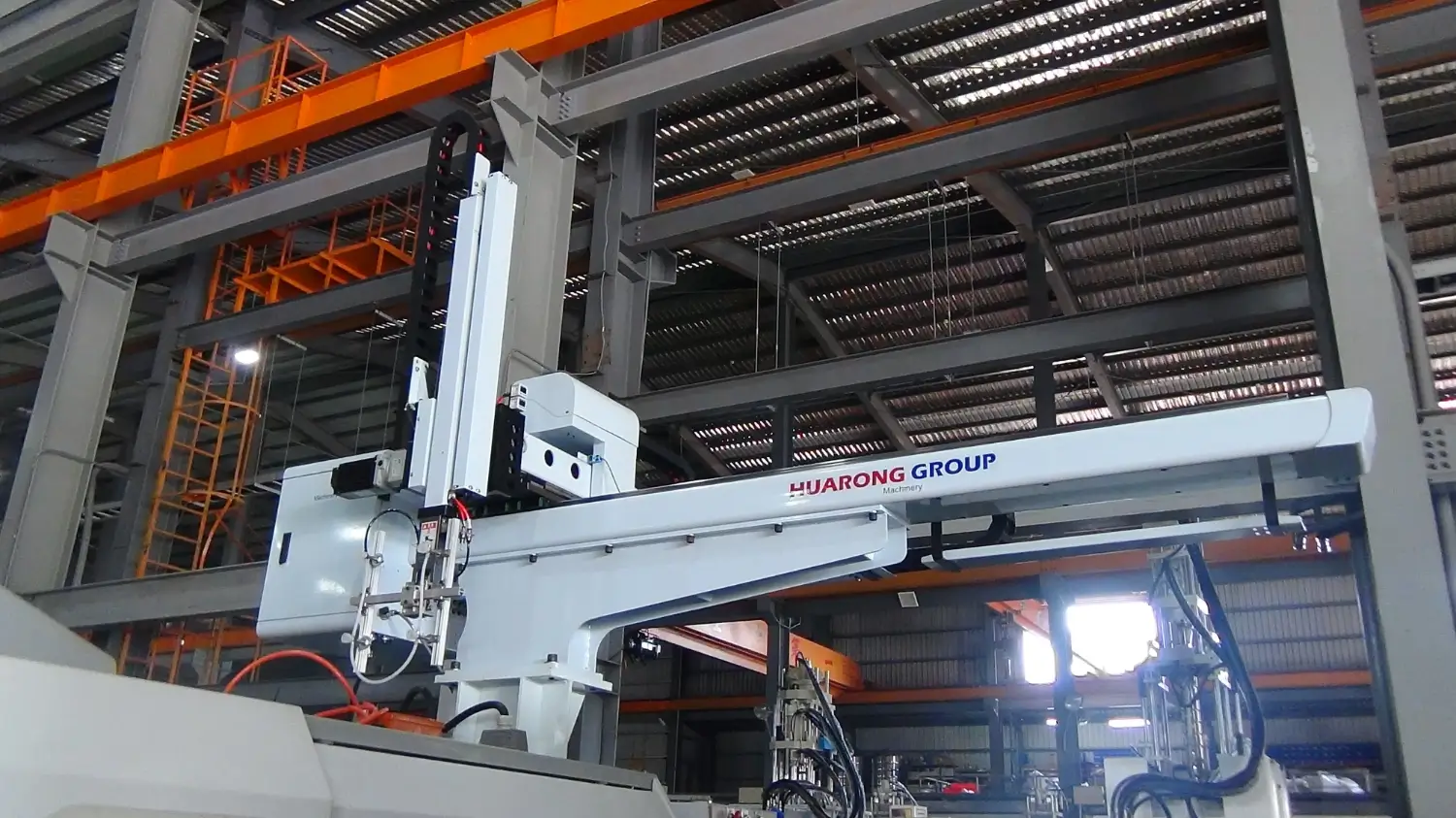
A robotic arm is a programmable multi-joint automation device capable of simulating human arm motion to perform diverse industrial tasks. With multiple joints and links, it achieves extension, rotation, grasping, and handling movements through precise control systems and real-time sensor feedback.
Unlike conventional equipment in the automation system, robotic arms offer programmability and flexibility. A simple change in the control program can instantly switch operations—from handling to welding or from assembly to packaging—greatly improving productivity and cost efficiency.
Related Reading: Comprehensive Guide to Injection Molding Robots: Automate Your Production Process
Related product: Injection Molding Robot - Manipulator Arm
Designing a high-performance robotic arm requires balancing precision, stability, flexibility, and safety. Below are its essential components:
| Component | Function Description |
|---|---|
| Joints & Links | Simulate rotation and extension; determine range of motion and degrees of freedom |
| End Effector | Performs interaction tasks (grippers, suction cups, welding torches, nozzles) |
| Actuators | Convert electric or hydraulic energy into motion (typically servo motors or pneumatic drives) |
| Sensors | Monitor position, angle, and pressure; provide real-time feedback |
| Controller | Serves as the “brain,” processing commands and controlling each axis precisely |
To ensure high-accuracy manufacturing, the design must address both structural rigidity and response sensitivity. Even a micron-level deviation can create defects in precision manufacturing—thus motion control and vibration damping are crucial.
The robotic arm operates through an integrated hardware-software control loop. Its five-stage workflow includes:
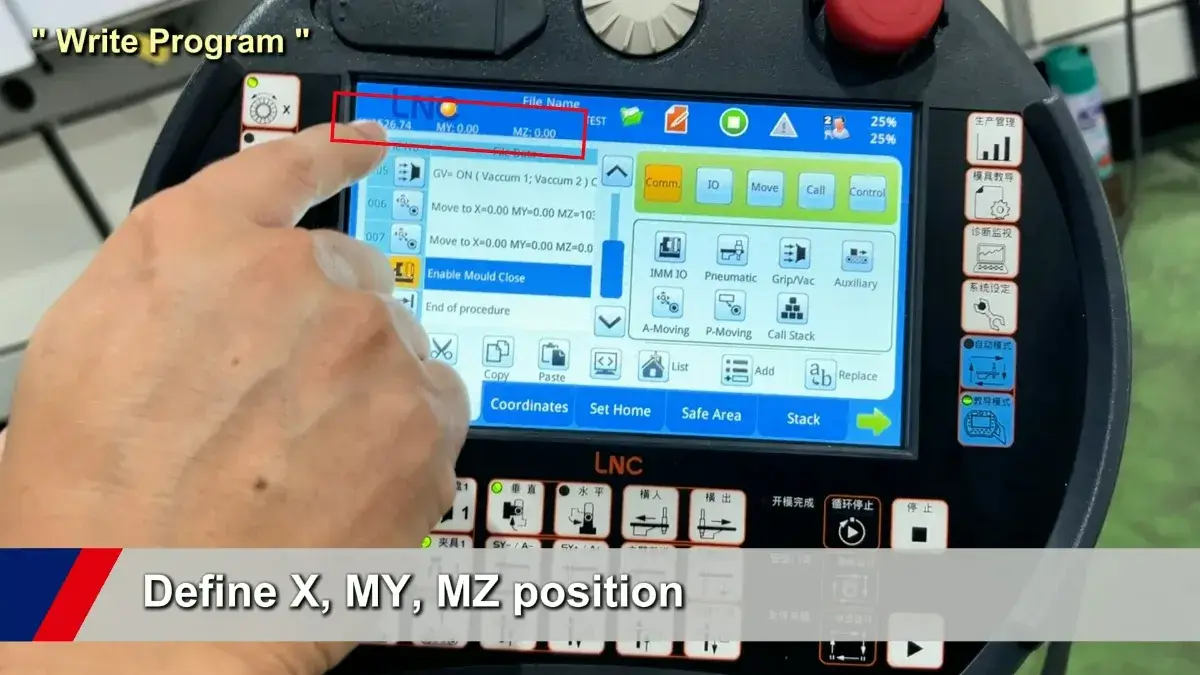
- Program Setup – Operators define trajectories, speeds, and sequences.
- Motion Drive – The controller sends commands to actuators.
- Data Feedback – Sensors report position and load data in real time.
- Motion Correction – The system self-adjusts to maintain precision.
- Task Execution – The end effector performs the action (e.g., gripping, welding, transferring).
This closed-loop control ensures stable, high-precision operations—even under variable loads or environments.
| Type | Key Features | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Cartesian | Linear movement on X-Y-Z axes, excellent positioning accuracy | CNC machining, 3D printing |
| SCARA | Fast and repeatable, ideal for horizontal tasks | Electronics assembly, labeling |
| Articulated | Multi-joint design similar to a human arm | Welding, painting, packaging |
| Delta | Triangular frame, ultrafast, lightweight | Food packaging, sorting |
| Collaborative (Cobot) | Safe interaction with humans, force sensors | SMEs, smart factories |
- Cartesian arms deliver linear accuracy and reliability.
- SCARA arms dominate in electronics assembly lines.
- Articulated arms offer the widest flexibility for automotive or metal applications.
- Delta arms enable rapid sorting for lightweight goods.
- Cobots mark the next stage of collaborative automation.
- Maximized Productivity: 24/7 consistent operation, reducing downtime.
- High Precision and Stability: Micron-level repeatability across complex cycles.
- Labor-Saving and Cost Reduction: Minimized manual work and long-term ROI improvement.
- Enhanced Safety: Operates safely in hazardous or confined environments.
- Flexible and Reconfigurable: Easily reprogrammed or adapted to new tooling.
Robotic arms handle welding, painting, and part assembly—ensuring consistent weld quality and uniform coating layers, which directly improve product reliability.
Essential for PCB insertion, micro-component placement, and testing tasks that require high precision and speed beyond human capability.
Automates sorting, boxing, and labeling to maintain hygiene while achieving high-speed throughput.
Performs surface finishing, composite layering, and complex component assembly—where precision and traceability are mission-critical.
Performs surface finishing, composite layering, and complex component assembly—where precision and traceability are mission-critical.
Related Reading: Assembly Robots: The Evolution and Future of Robot Assembly Lines
- AI Integration: Combining deep learning and vision systems will allow self-learning and adaptive path planning.
- Human-Robot Collaboration: Cobots will replace traditional cages, emphasizing cooperation instead of replacement.
- Sustainability & Efficiency: Lightweight materials, modular structures, and low-energy actuators align with ESG and green manufacturing goals.
- Cost & Implementation: While initial investment remains high, ROI grows rapidly with increased productivity and reduced defects.
The advancement of robotic arms is reshaping the manufacturing landscape, enabling industries to achieve faster, safer, and smarter production. As AI and sensing technologies evolve, robotic arms are becoming intelligent collaborators—capable of learning, adapting, and optimizing processes in real time.
At Huarong Group, we are an experienced injection molding machine manufacturer providing complete equipment solutions and full automation planning services. By integrating robotic arms with our injection molding systems, we help manufacturers worldwide achieve higher efficiency, stable quality, and long-term competitiveness in smart manufacturing.
- Group Name: Huarong Group
- Brand: Huarong, Yuhdak, Nanrong
- Service Offerings: Injection Molding Machine, Vertical Injection Molding Machine, Injection Molding Automation
- Tel: +886-6-7956777
- Address: No.21-6, Zhongzhou, Chin An Vil., Xigang Dist., Tainan City 72351, Taiwan
- Official Website: https://www.huarong.com.tw/