Common Injection Molding Defects: Causes, Types, and Solutions
2025-01-07 17:30:46

Injection molding defects are a critical challenge for manufacturers aiming to produce high-quality plastic products. These defects can lead to wasted materials, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the injection molding business, understanding the causes behind these issues and their solutions is essential. In this article, we'll explore the most common injection molding defects, categorize them into appearance, dimensional, and functional types, and offer actionable solutions to enhance your production process. Read on to optimize your manufacturing efficiency and minimize defects.
Injection molding defects can be broadly categorized into three main types: appearance defects, dimensional defects, and functional defects. Each category poses unique challenges and requires targeted solutions. Below, we dive into each type to help you identify, understand, and address these issues effectively.
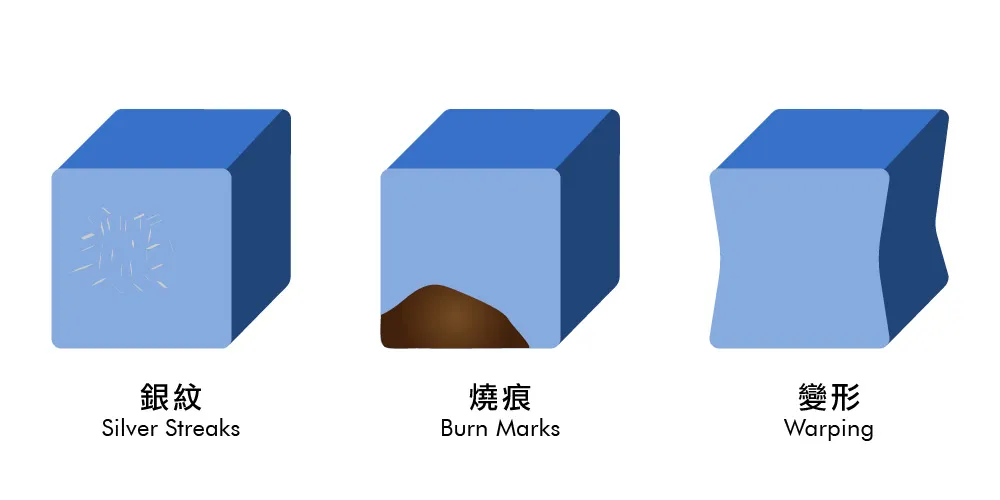
Appearance Defects
Appearance defects are the most visible flaws in injection-molded products, impacting their visual appeal and marketability. Common appearance defects include:
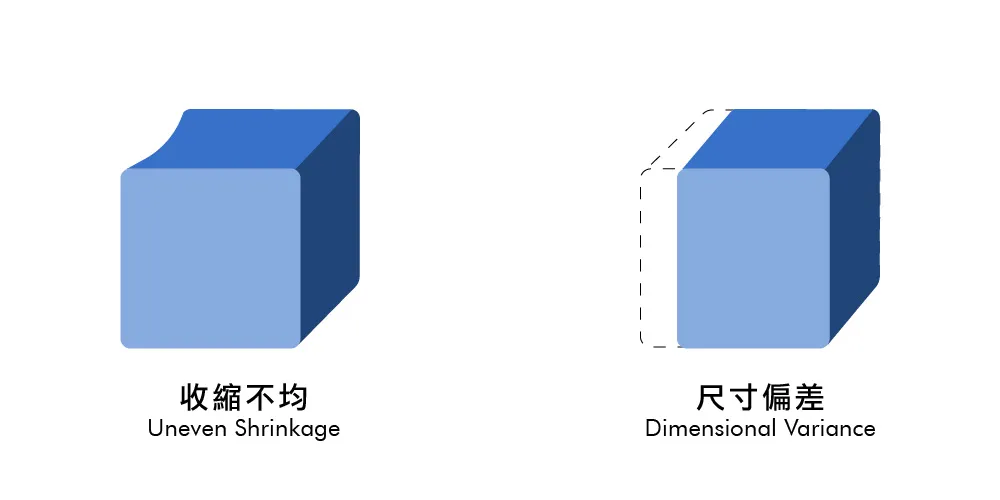
Dimensional Defects
Dimensional defects affect the size and fit of the final product, often leading to assembly issues. Key dimensional defects include:
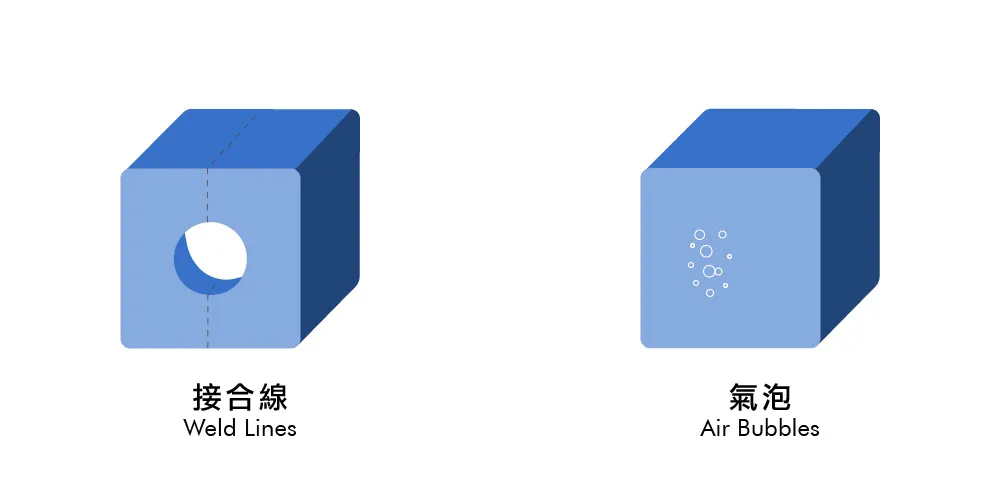
Functional Defects
Functional defects impact the usability and performance of the molded product. Examples include:
Injection molding defects often stem from controllable factors like machine settings, mold design, and material handling. Addressing these root causes can significantly reduce defect rates. Below are overarching strategies to prevent defects:
- Material Preparation: Ensure proper drying of raw materials to remove moisture and select materials with appropriate shrinkage and flow properties.
- Mold Design Optimization: Design molds with adequate venting, uniform cooling, and precise dimensions. Position gates strategically to ensure uniform material flow and minimize defects like weld lines and jetting.
- Process Parameter Adjustment: Regularly calibrate injection molding machines to maintain optimal settings. Monitor and adjust injection speed, pressure, and mold temperatures as needed.
- Cooling System Improvements: Enhance cooling channel designs to promote uniform temperature distribution and reduce defects like warping and shrinkage.
- Equipment Maintenance: Perform routine inspections of molds and machines. Replace worn components, such as screws, nozzles, and vents, to ensure consistent performance.
- Quality Assurance Practices: Implement real-time monitoring during production to detect anomalies early. Conduct post-production inspections to identify and address defects.
By adopting these preventive measures, manufacturers can enhance product quality, reduce waste, and improve operational efficiency.
Further reading: Injection Molding Machine Maintenance PDF and Checklist
Injection molding defects can disrupt production efficiency and quality, but understanding their causes and implementing the right solutions can make a significant difference. From addressing appearance issues like flow lines and burn marks to solving dimensional and functional defects such as shrinkage and weld lines, proactive measures are key to maintaining high standards in injection molding.
If you're ready to optimize your injection molding processes or invest in advanced injection molding machines, contact Huarong today. Together, we can minimize defects and maximize efficiency!
- Group Name: Huarong Group
- Brand: Huarong, Yuhdak, Nanrong
- Service Offerings: Injection Molding Machine, Vertical Injection Molding Machine, Injection Molding Automation
- Tel: +886-6-7956777
- Address: No.21-6, Zhongzhou, Chin An Vil., Xigang Dist., Tainan City 72351, Taiwan
- Official Website: https://www.huarong.com.tw/
Previous news : Huarong's Vision for 2025: Shaping a Sustainable Future in Injection Molding Technology
Next news : How to Repair an Injection Molding Machine: A Step-by-Step Guide