Hot Runner v.s. Cold Runner in Injection Molding:Key Differences & Mold Design
2026-01-09 13:17:33

In the plastic injection molding industry, the selection of the mold system not only affects product quality but also determines production efficiency and cost effectiveness. Hot runner and cold runner molds are the two most commonly used injection molding systems today, each with its own advantages and limitations. For manufacturers who require precise dimensional control, improved part quality, or pursue high-volume and high-efficiency production, understanding the operating principles, advantages, and disadvantages of both systems, as well as the factors that must be considered when making a selection, is the key to formulating an optimal manufacturing strategy.
Further reading:Sprue, Runner, and Gate in Injection Molding: A Practical Guide
The hot runner mold, also known as a runnerless mold or heated manifold system, uses heating devices inside the mold to deliver molten plastic from the injection machine nozzle to the part cavities, maintaining the runner temperature above the plastic melting point to ensure a molten state. The hot runner system is mainly composed of two parts:a heated manifold and nozzles. The manifold transports molten plastic parallel to the parting line above each cavity, while the nozzles, perpendicular to the manifold, deliver the molten material into the cavities. Hot runner systems can be divided into two types:
1. Insulated Runner System
- The runner itself is not heated and relies on thick channels and heat conduction to maintain the temperature of the molten material.
- Lower cost and allows rapid color changes, with more flexible material flow.
- Filling may be insufficient for large parts or plastics with long flow lengths.
2. Heated Runner System
- External heated runner:Uses external heating cores or heating plates to keep the material fully molten, with low heat loss, friendly to heat-sensitive materials, and convenient for color changes.
- Internal heated runner:Heating probes or heating tubes are installed inside the runner, using the insulating characteristics of molten plastic to reduce heat loss, but this requires higher injection pressure, makes color changes difficult, and heat-sensitive materials are prone to degradation.
Heating methods include heating coils, heater rods, heating tubes, and band heaters. Combined with multi-zone temperature control systems, they enable precise control of runner temperatures, ensuring uniform filling and stable part quality.
- High-speed cycle:Material remains molten in the runner, shortening the injection cycle and increasing productivity.
- High material utilization:Eliminates cold runner waste, saving raw materials and reducing subsequent recycling or processing costs.
- Precise quality control:Temperature and pressure can be controlled by zones, effectively reducing sink marks, weld lines, and warpage defects.
- Suitable for large parts and high production volumes:Large parts and mass production can maintain stable dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
- High initial mold cost and complex maintenance, requiring professional technicians for operation.
- Not suitable for heat-sensitive or easily degradable materials.
- Color changes can be challenging and may require additional cleaning and adjustment.
1. Injection pressure:Large parts or high-viscosity materials require flow simulation to ensure sufficient pressure.
2. Heating method:External heating systems are suitable for heat-sensitive materials, while internal heating systems are suitable for materials with high flow control requirements.
3. Nozzle and runner design:Different plastics and crystalline material types require appropriate runner sizes and nozzle designs.
4. Standardized or customized:Standard hot runner systems have lower costs, shorter lead times, and simpler maintenance; customized systems can meet special part requirements.
5. Multi-zone temperature control:Large molds or high-precision materials require multi-zone temperature control to compensate for heat loss and maintain uniform temperature.
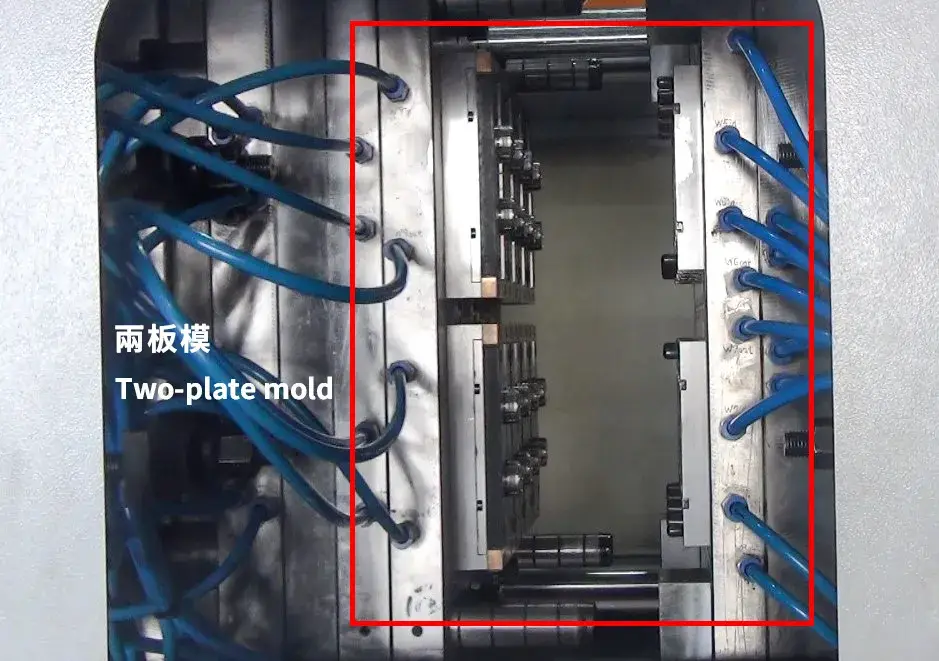
Cold runner molds are composed of two to three mold plates. Plastic is injected into the cavities through runners, and the runners themselves are not heated, causing the plastic to cool and solidify within the runner. Cold runner systems can be divided into two-plate molds and three-plate molds:
1. Two-plate mold
- The runner and the part are injected simultaneously, and an ejection system is required to separate the part from the runner.
- The mold structure is simple and suitable for conventional part designs.
2. Three-plate mold
- The runner and the part are located on different mold plates, allowing simultaneous ejection of the part and the runner.
- Suitable for complex parts or multi-cavity designs, but the mold structure is more complex, and maintenance requirements are slightly higher.
In cold runner systems, the runner is usually thicker than the part to ensure that the plastic can fill the cavity during cooling, preventing short shots or warpage. Cold runner waste must be recycled or reprocessed, increasing cycle time and operating costs.
- Low mold cost:Simple structure with low production and maintenance costs.
- Flexible operation:Easy to change colors and materials, especially suitable for heat-sensitive plastics.
- Wide material compatibility:Almost no limitations related to thermal stability.
- Easy maintenance:Mold disassembly, cleaning, and design modification are straightforward.
- Longer injection cycle time.
- Solidified runners form waste, increasing raw material consumption.
- Filling and consistency control for complex parts and large-sized parts are more difficult.
1. Runner size:The runner should be thicker than the part to ensure complete filling.
2. Gate type:Tunnel gates are commonly used and can automatically separate when the mold opens.
3. Nozzle and runner design:Cleaning accessibility must be considered to prevent solidification in dead corners.
4. Ease of mold maintenance:Simple designs facilitate daily maintenance and rapid material changes.
| Feature | Hot Runner System | Cold Runner System |
| Runner heating | Heated, maintains plastic in molten state | Not heated, plastic cools and solidifies |
| Injection cycle time | Short, high efficiency | Long, lower efficiency |
| Material waste | Almost none | Cold runner material generated and must be recycled or discarded |
| Applicable part size | Large parts and high production volumes | Small or medium-to-low production volume parts |
| Material applicability | Suitable for high-temperature plastics and non-heat-sensitive materials | Suitable for heat-sensitive materials or low-viscosity plastics |
| Color change | More difficult, requires runner cleaning | Simple and fast, no residual issues |
| Mold cost | High | Low |
| Maintenance difficulty | More complex | Simple |
| Precision control | High | Medium |
When deciding whether to use a hot runner or cold runner system, the following factors must be considered comprehensively:
1. Product size and complexity:Large or high-precision parts tend to use hot runners; small or simple parts tend to use cold runners.
2. Material characteristics:Heat-sensitive or easily degradable materials are recommended to use cold runners; high-temperature plastics and multi-color parts can use hot runners.
3. Production volume:High-volume or long-term production can offset the high investment cost of hot runners; low-volume, short-cycle, or trial production is more suitable for cold runners.
4. Cost and maintenance:Initial investment, material waste, energy consumption, and maintenance costs must be considered to conduct a cost-benefit analysis.
5. Process flexibility:If frequent color changes or rapid mold design adjustments are required, cold runners offer greater advantages.
Hot runner and cold runner systems each have their own advantages and limitations in the injection molding field. The selection of an appropriate mold system should be based on product characteristics, material properties, production volume, and cost effectiveness. By combining the recommendations of professional engineers and mold suppliers, manufacturers can achieve the optimal balance between quality, efficiency, and cost, ensuring maximum production benefits.
- Group Name: Huarong Group
- Brand: Huarong, Yuhdak, Nanrong
- Service Offerings: Injection Molding Machine, Vertical Injection Molding Machine, Injection Molding Automation
- Tel: +886-6-7956777
- Address: No.21-6, Zhongzhou, Chin An Vil., Xigang Dist., Tainan City 72351, Taiwan
- Official Website: https://www.huarong.com.tw/